
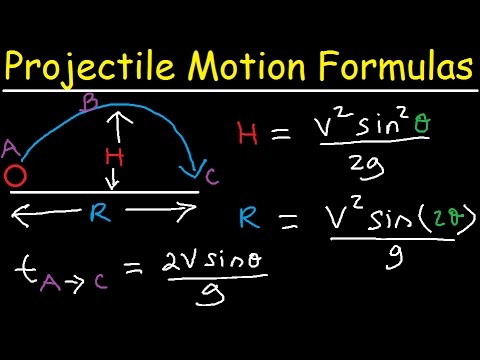
We have grown leaps and bounds to be the best Online Tuition Website in India with immensely talented Vedantu Master Teachers, from the most reputed institutions. Vedantu LIVE Online Master Classes is an incredibly personalized tutoring platform for you, while you are staying at your home. Question: If the horizontal range of a projectile is 4 times the maximum height attained by it, then the angle of projection is: Thus, distance covered with flow of the river = v r × t The Speed of the river, v r is equal to 3 km/h Therefore, the time is taken to cross the river = Width of the river / Speed of the river Speed of the guy = 4 km/h and width of the river = 1 km How long does it take him to traverse a 1.0 km wide river at 3.0 km/h while keeping his strokes parallel to the current? After he reaches the opposite bank, how far down the river does he go? Question: A guy can swim at a speed of 4.0 km/h in still water. The following is the equation:īecause this equation is similar to the parabola (y = ax + bx 2 ), it is concluded that that projectile motion is always parabolic in character. The trajectory equation is the path taken by a particle during projectile motion. OB = Horizontal component of velocity(u x ) * Total time(t) The horizontal range is a distance (OB) is: It is defined as the horizontal distance covered to the maximum distance possible. ( S = H max, v y = 0 and u y = u sin θ ) The vertical component of the velocity (V y ) will be zero when the ball reaches point A. It is the particle's highest point (point A).

Taking motion in Y direction, S y = u y t – 1/2(gt 2 ) In Y direction total displacement (S y ) = 0. It is the total amount of time the projectile remains in the air. G = Acceleration due to gravity (Taking it negative because gravity always work downward) The time of flight refers to the amount of time it takes a particle to travel from point A to point B.ĭifferential equations of motion can be used to discover various projectile motion parameters.Īpply the above equation for projectile motion, the equation will now be, H is defined as the height of the particle. Θ is defined as the angle of projection and Point O is defined as the point of projection. The projectile motion is divided into two parts: a horizontal motion with no acceleration and a vertical motion with constant acceleration due to gravity.Ĭonsider the following example of a ball being launched at an angle from point O to the horizontal x-axis with an initial velocity of u: Such an object is called a projectile and the curved path with which the projectile travels is what is termed as trajectory.įormulae related to a projectile that is launched at an oblique angle with respect to the horizontal and whose motion is referred with respect to the horizontal are:įormulas and Concepts of Projectile Motion Projectile motion is a form of motion experienced by an object or particle that is thrown near the Earth's surface and moves along a curved path under the action of gravity only (in particular, the effects of air resistance are assumed to be negligible). There are many types of motion around us. Football, baseball, cricket ball, and any other object are instances of projectile motion. The path that an object takes when thrown at an angle other than 90 degrees from a horizontal point is known as a trajectory, the object is known as a projectile, and the motion is defined as the projectile motion.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
